Bioflix activity gas exchange carbon dioxide transport – Delving into Bioflix Activity: Gas Exchange and Carbon Dioxide Transport, this exploration unveils the intricate processes that sustain life, from the exchange of gases in plants and animals to the transport of carbon dioxide in the bloodstream. Prepare to immerse yourself in a journey that unravels the fundamental mechanisms that drive biological processes.
Gas exchange, facilitated by structures like stomata and lenticels, plays a crucial role in the survival of living organisms. This activity delves into the intricacies of these processes, highlighting their significance in maintaining life’s delicate balance.
Bioflix Activity: Gas Exchange
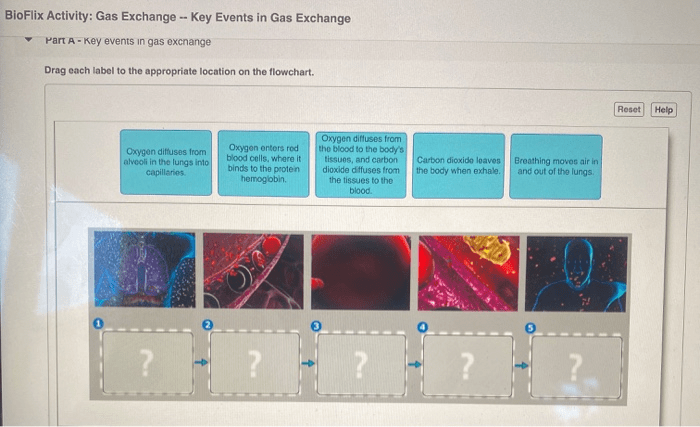
Gas exchange is a vital process for all living organisms, allowing for the uptake of oxygen and the release of carbon dioxide. In plants, gas exchange occurs through stomata, small pores found on the leaves. In animals, gas exchange takes place in the lungs, where oxygen is taken up from the air and carbon dioxide is released.
Role of Stomata and Lenticels in Gas Exchange, Bioflix activity gas exchange carbon dioxide transport
Stomata are small pores found on the surface of plant leaves. They allow for the exchange of gases between the plant and the atmosphere. Stomata open and close to regulate the amount of gas exchange that occurs. Lenticels are similar to stomata, but they are found on the stems of plants.
They also allow for the exchange of gases between the plant and the atmosphere.
Examples of How Gas Exchange is Essential for Life
- In plants, gas exchange is essential for photosynthesis.Photosynthesis is the process by which plants use sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose. Glucose is a sugar that plants use for energy.
- In animals, gas exchange is essential for cellular respiration.Cellular respiration is the process by which animals use oxygen to break down glucose for energy.
Carbon Dioxide Transport
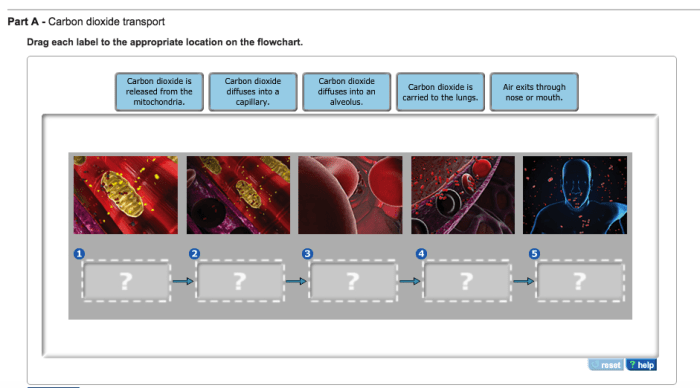
Carbon dioxide is a waste product of cellular respiration. It must be transported from the cells to the lungs, where it can be exhaled. There are three main mechanisms of carbon dioxide transport in the blood:
Simple Diffusion
Simple diffusion is the movement of a substance from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. Carbon dioxide diffuses from the cells into the blood plasma, where it is then transported to the lungs.
Carbaminohemoglobin
Carbaminohemoglobin is a compound formed when carbon dioxide reacts with hemoglobin, the protein that carries oxygen in the blood. Carbaminohemoglobin transports about 10% of the carbon dioxide in the blood.
Bicarbonate
Bicarbonate is a compound formed when carbon dioxide reacts with water. Bicarbonate is transported in the blood plasma. About 70% of the carbon dioxide in the blood is transported as bicarbonate.
Factors that Affect the Rate of Carbon Dioxide Transport
- The partial pressure of carbon dioxide– The partial pressure of carbon dioxide is the concentration of carbon dioxide in the blood. The higher the partial pressure of carbon dioxide, the faster the rate of carbon dioxide transport.
- The pH of the blood– The pH of the blood affects the rate of carbon dioxide transport. A lower pH (more acidic) increases the rate of carbon dioxide transport.
- The temperature of the blood– The temperature of the blood affects the rate of carbon dioxide transport. A higher temperature increases the rate of carbon dioxide transport.
Carbon Dioxide Utilization
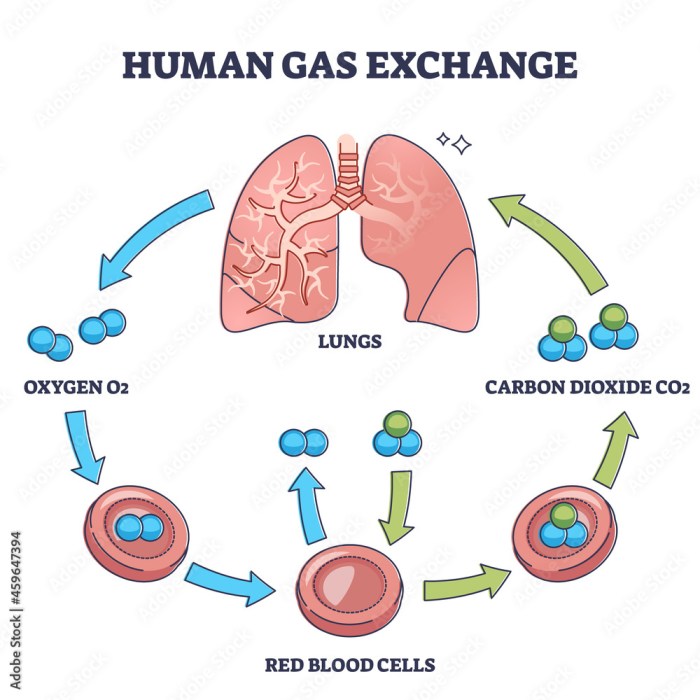
Carbon dioxide is a waste product of cellular respiration, but it is also an important resource for plants and animals. Plants use carbon dioxide for photosynthesis, the process by which they convert sunlight into energy. Animals use carbon dioxide to produce bicarbonate, which is used to buffer the blood.
Role of Carbon Dioxide in Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants use sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose. Glucose is a sugar that plants use for energy. The chemical equation for photosynthesis is:
CO2+ 6H 2O + light energy → C 6H 12O 6+ 6O 2
Role of Carbon Dioxide in Cellular Respiration
Cellular respiration is the process by which animals use oxygen to break down glucose for energy. The chemical equation for cellular respiration is:
C6H 12O 6+ 6O 2→ 6CO 2+ 6H 2O + energy
Examples of How Carbon Dioxide is Used in Industrial Processes
- Carbon dioxide is used to produce carbonated beverages.
- Carbon dioxide is used to produce dry ice.
- Carbon dioxide is used to produce plastics.
Query Resolution: Bioflix Activity Gas Exchange Carbon Dioxide Transport
What is the significance of gas exchange in plants?
Gas exchange in plants is essential for photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert sunlight into energy. It allows plants to absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and release oxygen as a byproduct.
How does carbon dioxide transport occur in the blood?
Carbon dioxide is transported in the blood in two primary forms: dissolved in plasma and bound to hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is a protein in red blood cells that binds to carbon dioxide, increasing the blood’s capacity to carry this waste product.
What factors affect the rate of carbon dioxide transport?
The rate of carbon dioxide transport is influenced by several factors, including temperature, pH, and the concentration of carbon dioxide in the blood.