Life expectancy ap human geography definition refers to the average number of years that a person is expected to live based on current mortality rates. It is a crucial indicator of a population’s health and well-being, reflecting the complex interplay of factors such as socioeconomic conditions, healthcare systems, and environmental influences.
This concept provides insights into the overall health and quality of life of a population, enabling policymakers and researchers to make informed decisions aimed at improving public health outcomes and promoting longevity.
Define Life Expectancy
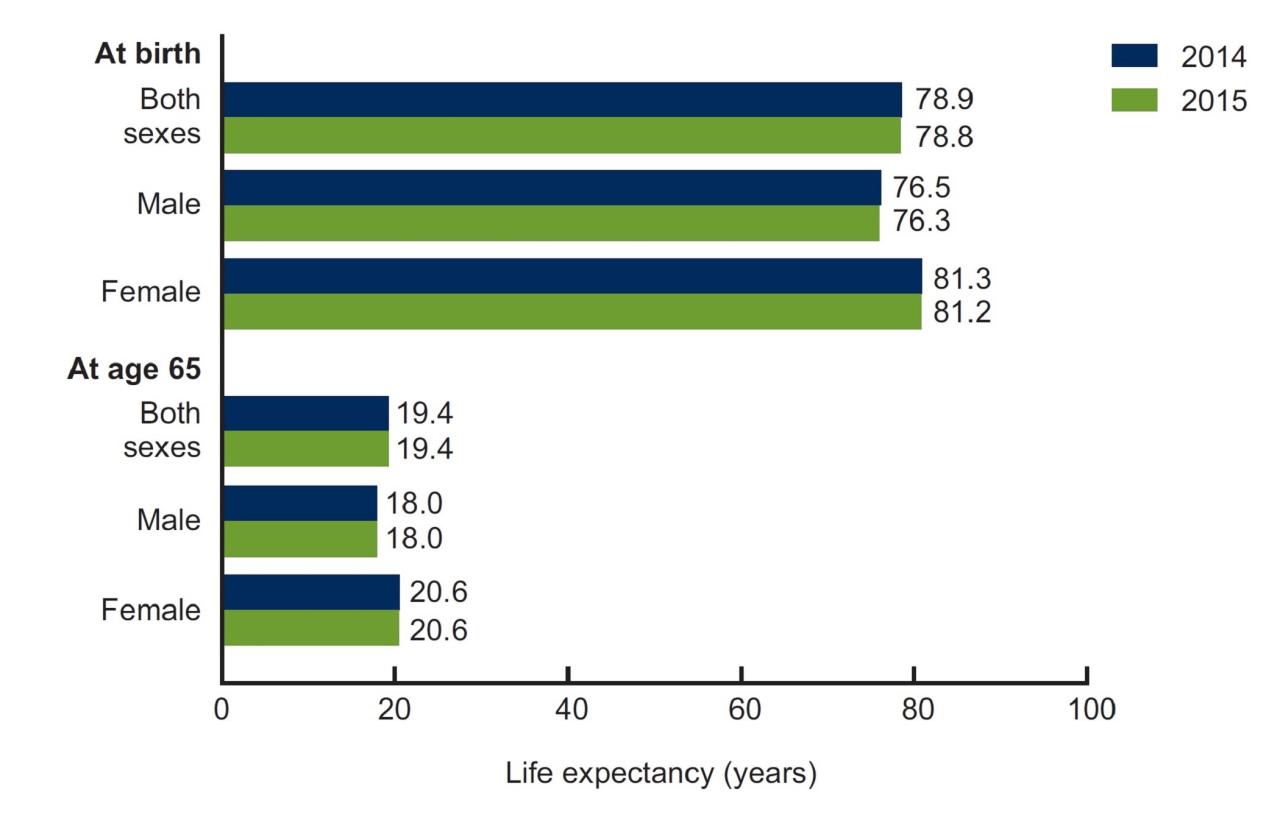
Life expectancy is a statistical measure of the average number of years that a person is expected to live, based on the current mortality rates and patterns in a given population.
Factors Influencing Life Expectancy
- Socioeconomic factors: income, education, access to healthcare
- Environmental factors: air pollution, water quality, sanitation
- Healthcare systems: availability and quality of healthcare
- Lifestyle factors: smoking, alcohol consumption, physical activity
How Life Expectancy is Measured
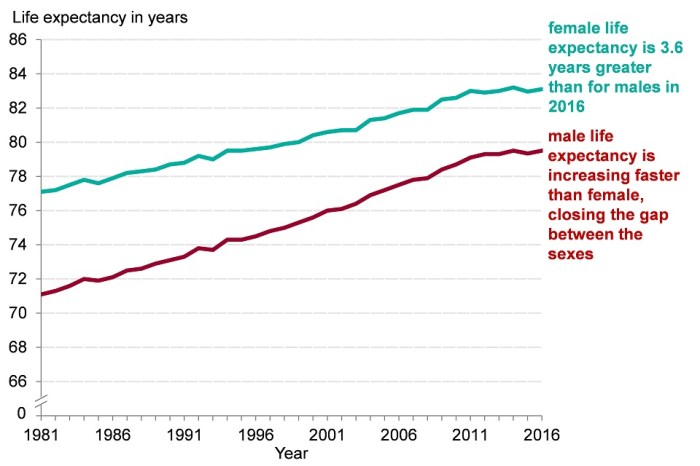
Life expectancy is typically measured using mortality tables, which track the number of deaths at each age in a given population.
Limitations of these methods include:
- Incomplete data, especially in developing countries
- Assumption of constant mortality rates over time
Challenges of Measuring Life Expectancy in Developing Countries, Life expectancy ap human geography definition
- Lack of reliable data on deaths and population
- High levels of infant mortality
- Rapid changes in mortality rates
Factors Affecting Life Expectancy
The key factors affecting life expectancy include:
- Income and poverty
- Education
- Healthcare
- Nutrition
- Environmental factors
These factors interact in complex ways to influence life expectancy.
Global Patterns of Life Expectancy
Life expectancy varies significantly around the world.
Regions with the highest life expectancies include:
- Japan (84.3 years)
- Monaco (83.6 years)
- Singapore (83.1 years)
Regions with the lowest life expectancies include:
- Central African Republic (49.4 years)
- Chad (52.3 years)
- Sierra Leone (52.7 years)
These patterns are influenced by factors such as income, education, healthcare systems, and environmental conditions.
Trends in Life Expectancy
Life expectancy has increased significantly over the past century due to advances in healthcare, nutrition, and sanitation.
However, there are concerns that life expectancy may be declining in some countries due to factors such as obesity, smoking, and environmental pollution.
Implications of Life Expectancy: Life Expectancy Ap Human Geography Definition

Life expectancy has important implications for individuals, societies, and governments.
- Retirement planning
- Healthcare costs
- Economic growth
- Social security systems
Changing life expectancies can have significant economic, social, and political consequences.
Expert Answers
What is the difference between life expectancy and life span?
Life expectancy refers to the average number of years a person is expected to live, while life span refers to the maximum potential age a human can reach.
How is life expectancy calculated?
Life expectancy is calculated using mathematical models that consider factors such as mortality rates, age distribution, and population growth.
What are the key factors that affect life expectancy?
Factors influencing life expectancy include socioeconomic conditions, healthcare systems, environmental factors, nutrition, and lifestyle choices.