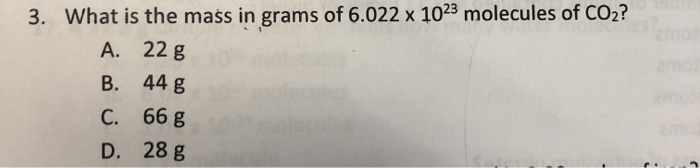How many molecules are in 2.50 moles of sio2 – Unveiling the molecular realm within 2.50 moles of silicon dioxide (SiO2), this exploration embarks on a journey to quantify its constituent particles. SiO2, a ubiquitous material in various industries, presents a captivating subject for investigating the fundamental relationship between moles and the number of molecules they encompass.
Delving into the intricacies of chemistry, we unravel the concept of the mole as a cornerstone unit for measuring the quantity of a substance. By harnessing Avogadro’s number, a pivotal constant, we establish a bridge between the macroscopic realm of moles and the microscopic world of individual molecules.
Definition and Explanation of Mole: How Many Molecules Are In 2.50 Moles Of Sio2
A mole is a fundamental unit of measurement in chemistry that represents a specific quantity of a substance. It is defined as the amount of substance that contains exactly 6.02214076 × 10 23elementary entities, which can be atoms, molecules, ions, or electrons.
The mole concept is essential for quantifying the amount of reactants and products in chemical reactions, as well as for determining the concentration of solutions and the stoichiometry of chemical compounds.
Calculating the Number of Molecules in a Given Number of Moles
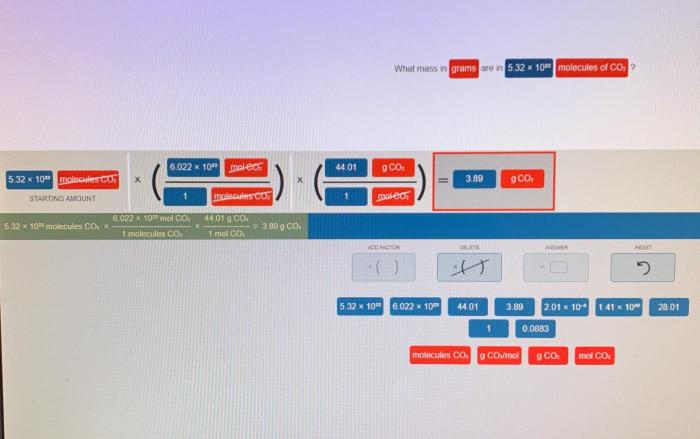
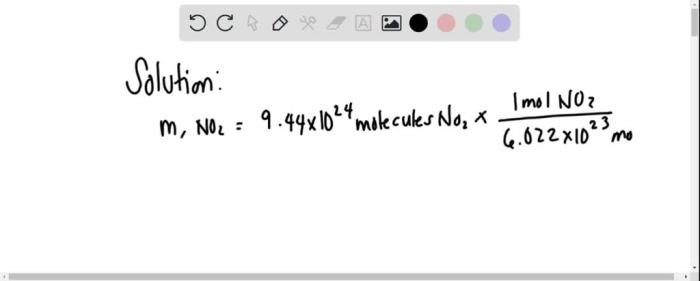
The number of molecules in a given number of moles can be calculated using Avogadro’s number, which is the number of elementary entities present in one mole of a substance.
The formula for calculating the number of molecules ( N) in a given number of moles ( n) is:
N= n× NA
where NAis Avogadro’s number.
To calculate the number of molecules in 2.50 moles of SiO 2:
- n= 2.50 mol
- NA= 6.02214076 × 10 23molecules/mol
Therefore, the number of molecules in 2.50 moles of SiO 2is:
N= 2.50 mol × 6.02214076 × 10 23molecules/mol = 1.50553519 × 10 24molecules
Properties and Applications of SiO2, How many molecules are in 2.50 moles of sio2
Silicon dioxide (SiO 2), also known as silica, is a colorless, crystalline solid that is found in nature as sand, quartz, and other minerals.
SiO 2has a high melting point, low thermal conductivity, and excellent electrical insulation properties. These properties make it a valuable material for various applications, including:
- Glass production
- Electronics (as an insulator in transistors and integrated circuits)
- Construction (as a component of cement and concrete)
- Healthcare (as a filler in medical devices and drug delivery systems)
Chemical Reactions Involving SiO2
SiO 2is a relatively inert substance, but it can react with certain chemicals under specific conditions.
One common reaction involving SiO 2is the formation of silicates, which are compounds that contain silicon and oxygen. Silicates are found in a wide variety of minerals, including asbestos, granite, and feldspar.
SiO 2can also react with certain acids to produce glass. Glass is a non-crystalline solid that is formed when SiO 2is heated to a high temperature and then cooled rapidly.
Question & Answer Hub
What is the significance of Avogadro’s number in this context?
Avogadro’s number serves as a crucial conversion factor, enabling us to bridge the gap between the macroscopic quantity of moles and the microscopic realm of individual molecules.
How does the number of molecules in 2.50 moles of SiO2 relate to its properties?
The number of molecules in a given quantity of SiO2 directly influences its physical and chemical properties. For instance, a higher molecular abundance typically translates to increased density, viscosity, and thermal conductivity.