Which of the following is not a product cost – In the realm of accounting, distinguishing between product costs and non-product costs is crucial for accurate financial reporting. This introductory paragraph delves into the intricacies of product costs, exploring their definition, characteristics, and significance.
Product costs, as the name suggests, are expenses directly related to the production of goods or services. They encompass raw materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead. These costs are capitalized as inventory assets and subsequently recognized as expenses when the related products are sold.
Product Costs Overview
Product costs are expenses directly attributable to the production of goods. These costs are incurred during the manufacturing process and are considered part of the cost of goods sold (COGS). Product costs are crucial for determining the profitability of a business and are essential for financial reporting and decision-making.
Categories of Product Costs
- Direct Material Costs:Raw materials and components used in the production of goods.
- Direct Labor Costs:Wages and benefits paid to employees directly involved in the production process.
- Manufacturing Overhead Costs:Indirect costs associated with production, such as factory rent, utilities, and depreciation on production equipment.
Examples of Product Costs
- Steel used in the production of automobiles
- Wages paid to assembly line workers
- Factory electricity costs
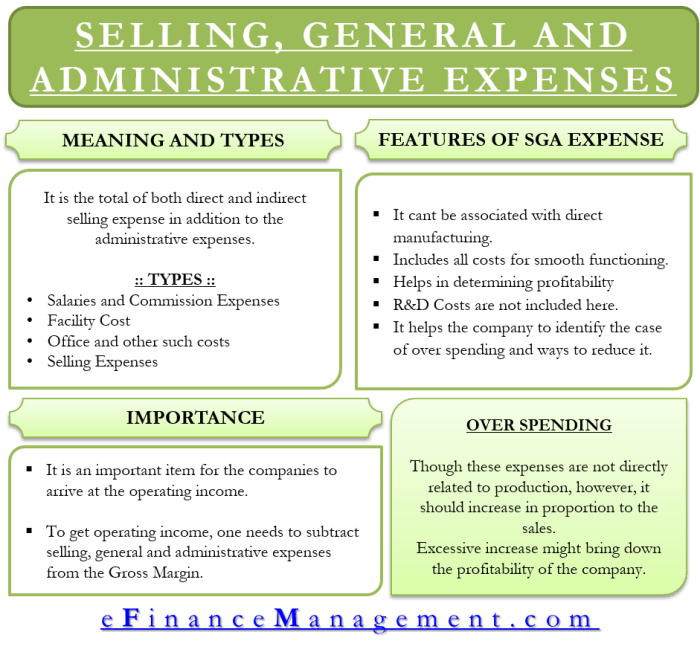
Non-Product Costs
Non-product costs are expenses that are not directly related to the production of goods. These costs are incurred during the period but are not included in COGS. Non-product costs are often referred to as period costs or operating expenses.
Types of Non-Product Costs
- Selling and Marketing Expenses:Costs associated with promoting and selling products, such as advertising, sales commissions, and trade show expenses.
- Administrative Expenses:Costs related to the general administration of the business, such as salaries of administrative staff, office rent, and legal fees.
- Research and Development Expenses:Costs incurred in developing new products or processes.
Examples of Non-Product Costs, Which of the following is not a product cost
- Advertising campaigns
- Salaries of office staff
- Research and development costs for new products
Distinguishing Between Product and Non-Product Costs: Which Of The Following Is Not A Product Cost
Correctly classifying costs as product or non-product is essential for accurate financial reporting and decision-making. The following table summarizes the key differences between these two types of costs:
| Characteristic | Product Costs | Non-Product Costs |
|---|---|---|
| Directly related to production | Yes | No |
| Included in COGS | Yes | No |
| Expensed in the period incurred | No | Yes |
| Affect inventory valuation | Yes | No |
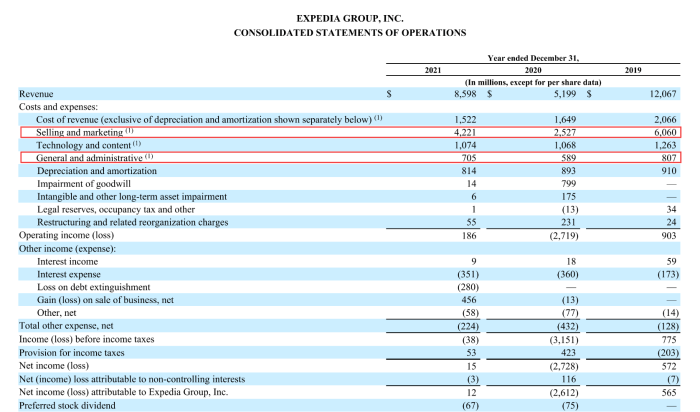
The implications of misclassifying costs can be significant. For example, if product costs are incorrectly classified as non-product costs, the COGS will be understated, resulting in an overstatement of net income. Conversely, if non-product costs are incorrectly classified as product costs, the COGS will be overstated, resulting in an understatement of net income.
Examples of Costs Not Considered Product Costs
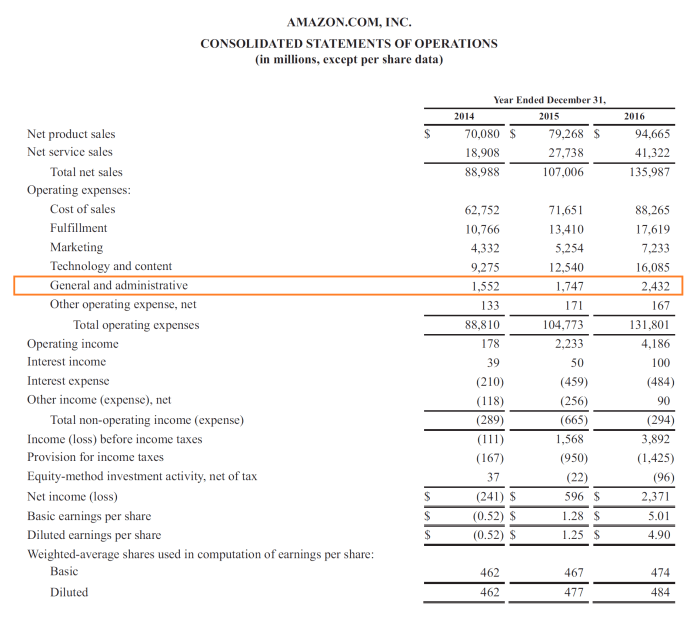
- Interest Expense:Costs associated with borrowing money, such as interest on loans and bonds.
- Income Taxes:Taxes paid on business income.
- Depreciation on Office Equipment:Costs associated with the use of office equipment, such as computers and desks.
These costs are not considered product costs because they are not directly related to the production of goods. Interest expense is a financing cost, income taxes are a legal obligation, and depreciation on office equipment is an administrative cost.
FAQ Summary
What are the key differences between product costs and non-product costs?
Product costs are directly related to production, while non-product costs are indirect expenses not involved in manufacturing.
Why is it important to correctly classify costs as product or non-product?
Correct classification ensures accurate calculation of cost of goods sold and net income, leading to reliable financial statements.