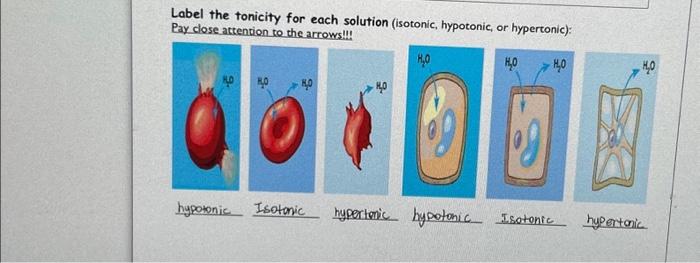
Label the tonicity for each solution – Labeling the tonicity of solutions is a crucial aspect of understanding the behavior of solutions in biological and chemical systems. Tonicity refers to the relative concentration of solutes in a solution compared to another solution, and it plays a significant role in various cellular processes and applications.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of tonicity, including its definition, types, and methods for labeling the tonicity of solutions. Additionally, it explores the factors affecting tonicity and its applications in various fields.
Solution Concentration
Solution concentration refers to the amount of solute dissolved in a given amount of solvent. It can be expressed in various units, including molarity (M), molality (m), and mass percentage (%). Solutions with higher concentrations contain more solute per unit volume or mass of solvent.
Tonicity
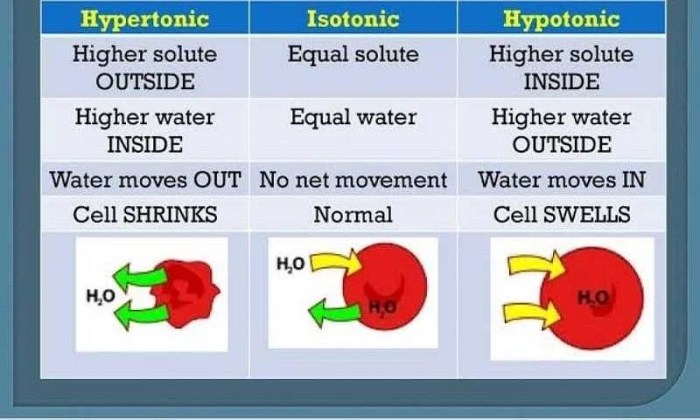
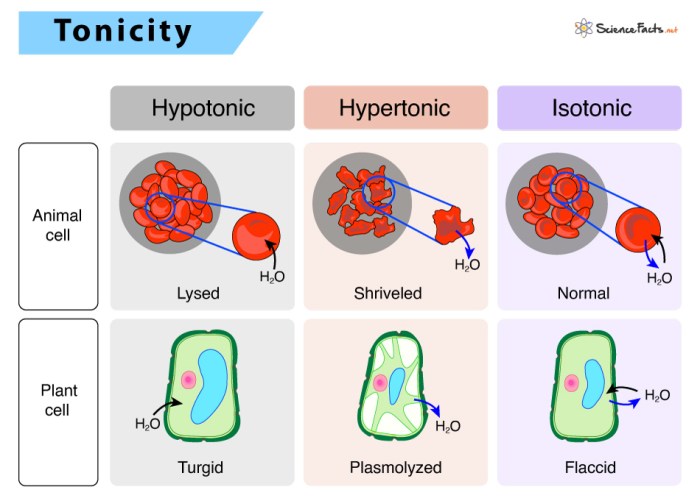
Tonicity measures the relative concentration of solutes across a semipermeable membrane. It determines the movement of water between two solutions and has a significant impact on cell function. There are three types of tonicity: hypotonic, hypertonic, and isotonic.
Hypotonic Solution, Label the tonicity for each solution
A hypotonic solution has a lower concentration of solutes than the cell. Water moves into the cell, causing it to swell and potentially burst.
Hypertonic Solution
A hypertonic solution has a higher concentration of solutes than the cell. Water moves out of the cell, causing it to shrink and potentially die.
Isotonic Solution
An isotonic solution has the same concentration of solutes as the cell. There is no net movement of water, and the cell maintains its normal shape and function.
Labeling Tonicity
To determine the tonicity of a solution, compare its concentration to the concentration of the cell it will interact with. A solution is:
- Hypotonic if its concentration is lower than the cell.
- Hypertonic if its concentration is higher than the cell.
- Isotonic if its concentration is the same as the cell.
Factors Affecting Tonicity
Several factors can affect the tonicity of a solution:
Solute Concentration
The higher the concentration of solute, the more hypertonic the solution.
Temperature
Higher temperatures increase the kinetic energy of water molecules, making them more likely to move across a semipermeable membrane, potentially altering tonicity.
Pressure
Applying pressure can affect the movement of water across a semipermeable membrane, influencing tonicity.
Applications of Tonicity
Tonicity plays a crucial role in various biological processes and has applications in:
Medicine
Tonicity is considered in intravenous fluids, dialysis solutions, and cell culture media to maintain cell health and function.
Biotechnology
Tonicity is important in cell preservation, genetic engineering, and drug delivery systems.
Environmental Science
Tonicity affects the survival and distribution of organisms in aquatic environments, such as freshwater and saltwater ecosystems.
Expert Answers: Label The Tonicity For Each Solution
What is the significance of tonicity in biological systems?
Tonicity plays a crucial role in maintaining cell volume and regulating water movement across cell membranes. Hypotonic solutions can cause cells to swell and burst, while hypertonic solutions can lead to cell shrinkage.
How does temperature affect tonicity?
Temperature can influence tonicity by affecting the solubility of solutes. Generally, increasing temperature increases the solubility of solutes, which can lead to changes in tonicity.